GBP/USD tumbles as markets pivot into safe havens on rising Middle East tensions
- The Israel-Iran conflict is heating up, pummeling broad-market risk appetite.
- US President Donald Trump is weighing stepping into the altercation directly, further hitting market stability.
- Key US Retail Sales missed expectations ahead of a key double-header central bank showing.
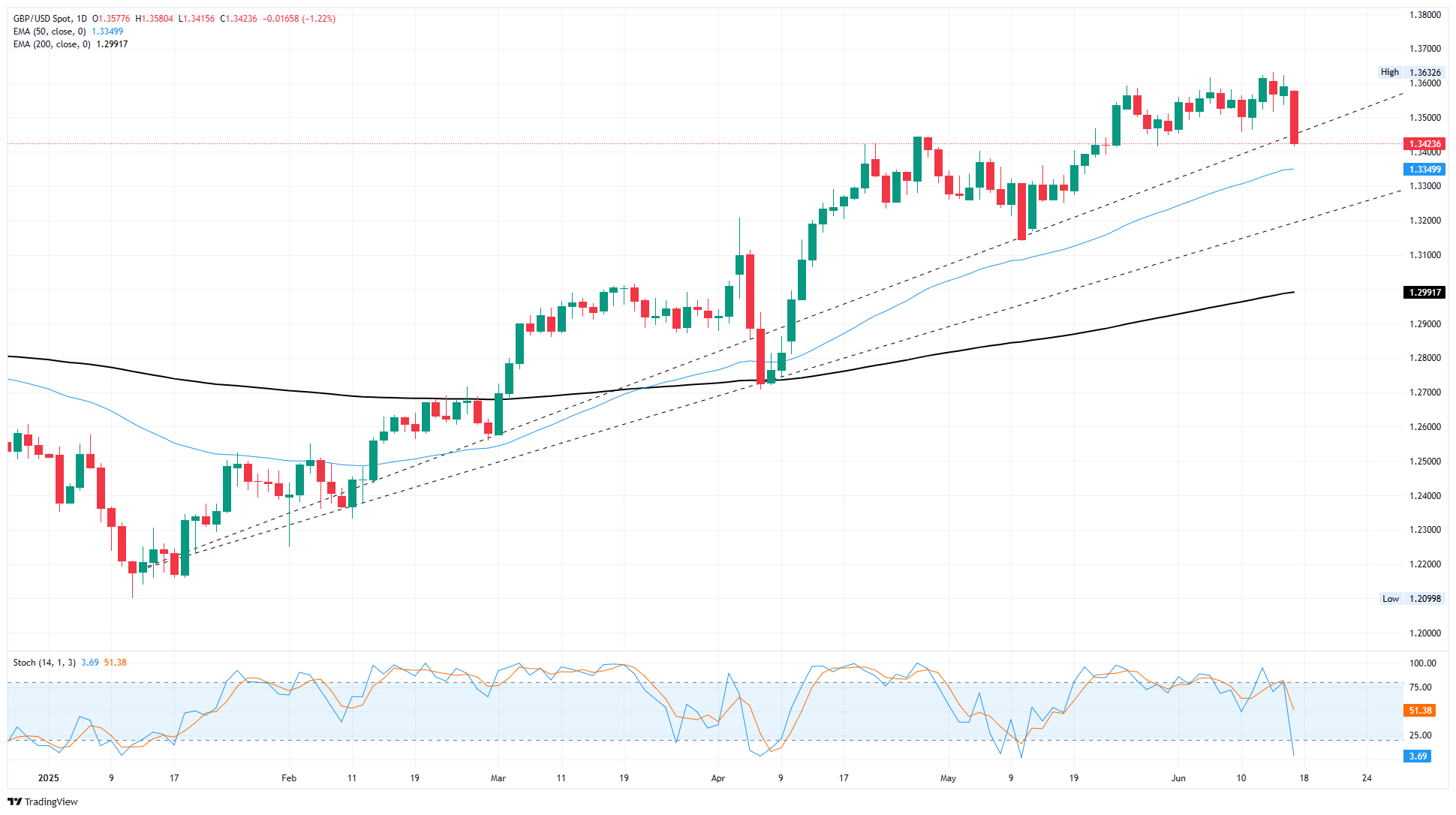
GBP/USD plummeted over 1.2% on Tuesday, backsliding through near-term congestion and popping out the other side near the 1.3400 handle after global investors were knocked off their pre-seeded hopes that the Israel-Iran altercation would find a quick and peaceful resolution.
Donald Trump, posting on social media Tuesday, declared that he wants an “UNCONDITIONAL SURRENDER” from Iranian supreme leader Ali Khamenei, and announced that American military assets were moving into the Middle East conflict region. The escalation between Israel and Iran, on top of Trump’s decision to further involve American military assets and personnel, has investors on edge as their previous hopes for a quick resolution wither on the vine. The Trump administration has a poor track record for successfully resolving geopolitical issues, both internal and external, despite the Trump team’s insistence on getting involved structurally in complex issues both at home and abroad.
US Retail Sales figures for the month of May contracted sharply, falling 0.9% MoM as consumer spending continues to slow. It is the second time this year that aggregated Retail Sales figures have contracted nearly a full percent, and previous data also saw downside revisions. While Retail Sales data doesn’t carry the market-moving weight of other key indicators, such as inflation or net monthly job gains, it is still a key factor that the Federal Reserve (Fed) weighs when considering interest rate adjustments. Broad-market bets for the next Fed rate cut are still holding out for a September rate trim; however, odds of at least a quarter-point cut have declined to nearly 50% this week.
US President Donald Trump has gotten increasingly vocal about his wishlist to have the Fed start dropping interest rates, even as Fed policymakers hold in their “wait and see” stance as officials brace for economic fallout from Trump’s whipsaw tariff “strategy”. The BoE is likewise expected to hold rates steady at 4.25%, but no meaningful shifts in policy stances, or complaints about them, are expected. The Fed reveals its latest rate call on Wednesday, with the BoE slated for early Thursday.
GBP/USD price forecast
Cable’s decline on Tuesday puts GBP/USD on pace to take a fresh bear run at the 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near 1.3350, but only if bearish momentum continues. GBP/USD has tended to fade bearish snaps through 2025, with the pair still finding technical support from a rising trendline drawn from January’s lows near 1.2100.
GBP/USD daily chart
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.



